42. Fundamentals of Transistor With Built-In Resistors
The transistor with built-in resistor is the one that resistors equipped to bipolar transistor, oftenly called as digital transistor.
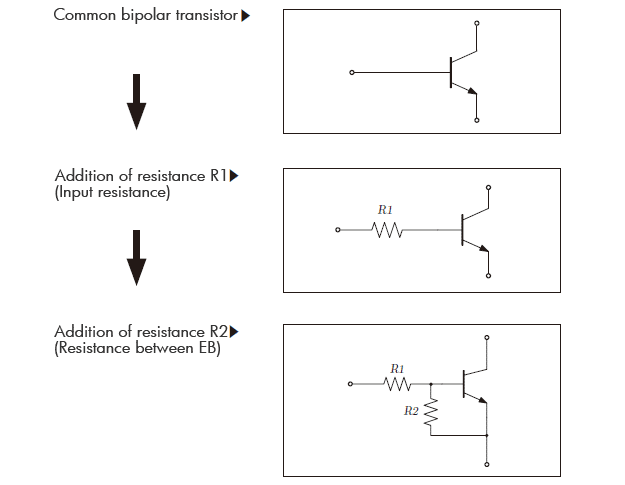
(1) About resistance R1
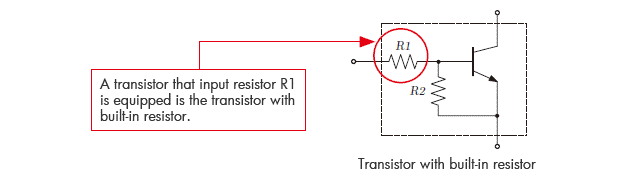
The role of resistor R1: The performance of the transistor is stabilized by converting the input voltage into the current. The performance of bipolar transistor is unstable if voltage such as output of IC is directly applied on the base terminal. The operation can be stabilized when it is made to operate as current control by putting resistor (input resistor) between IC and the base terminal. This is because of output current change in linear by base current control while it is exponential change by voltage control. A transistor that input resistor R1 is equipped is the transistor with built-in resistor.
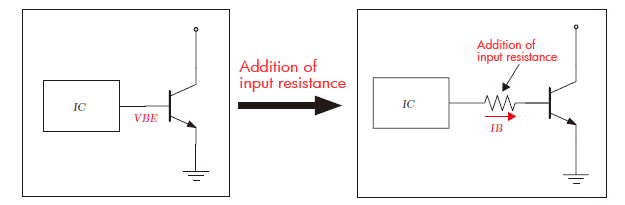
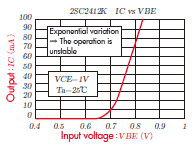
Operation is unstable.
Operation is unstable in the input
voltage (The output current changes exponentially in the input
voltage).
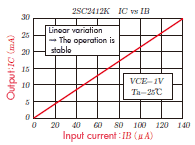
Operation is stable.
The operation
stabilize when adding input resistance and made the input to
electric current (Base current:IB). (The output current changes
into linear for the input current.)
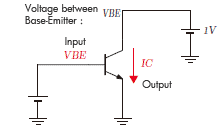
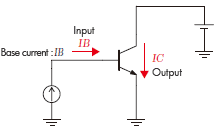
Compares the operation of transistor when the input is the voltage, and when the input is current.
|
Voltage control Input: Voltage VEB between emitter-base |
Current control Input: Base current IB |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Is:Constant determined by device Exponential changes |
hFE:Amplification factor Linear changes |
|
|
|
|
It is understood that the output changes exponentially to the input in the left voltage control while the output changes linear to the input in right when seen the input-output characteristic. In other words, in the voltage control the output current is greatly changed by the slight changes in input, and operation becomes unstable. For example, the right graph, output current becomes double from from 9mA to 18mA when the input current changes double from 40 μ A to 80 μ A however, in the left graph the output current becomes 7 times from 10mA to 70mA when the input voltage changes slightly by 14% from 0.7V to 0.8V. Under such circumstances, it is not suitable for actual use because the output current changes greatly when there is slight noise in the input voltage.
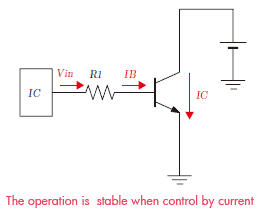
Thus, bipolar transistor requires the input resistance R1 to convert the voltage output from IC to the base current as the current control is more stabilized.So digital transistor is suitable to reduce the product points, space because it is inbuilt with this R1.
(2)About resistance R2
The role of resistance R2: It absorbs the leak current, and prevents the malfunction. Resistance R2 prevents the transistor from malfunctioning by dropping the leak current and the noise that entered from the input to the ground.
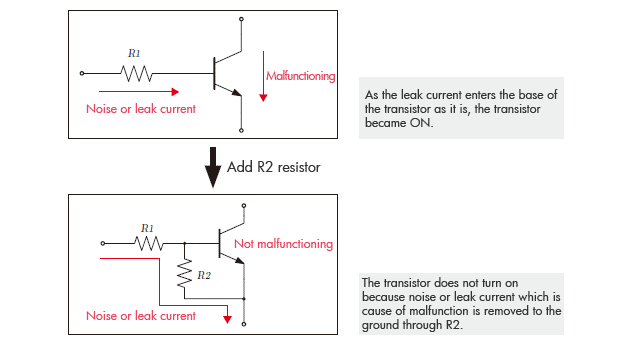
Input currents will all fall on the ground if it is a minute current, if the input current is large, then a large portion of the input current will start entering the the base of the transistor, and ON the transistor.
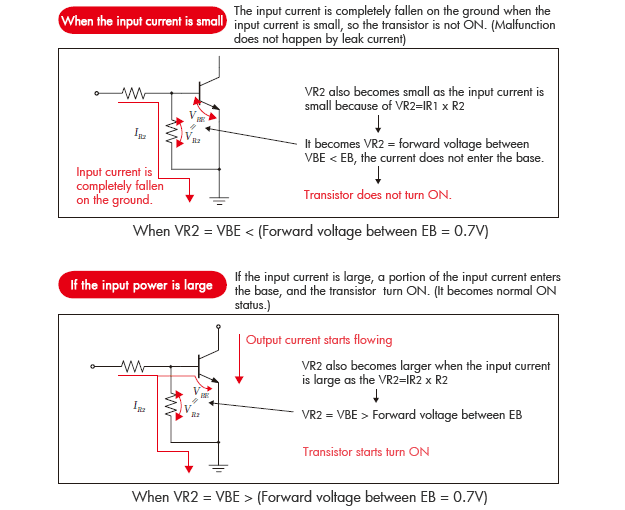
Thus, the stable operation is achieved by resistance R2, although voltage of certain level is required to turn on the transistor.